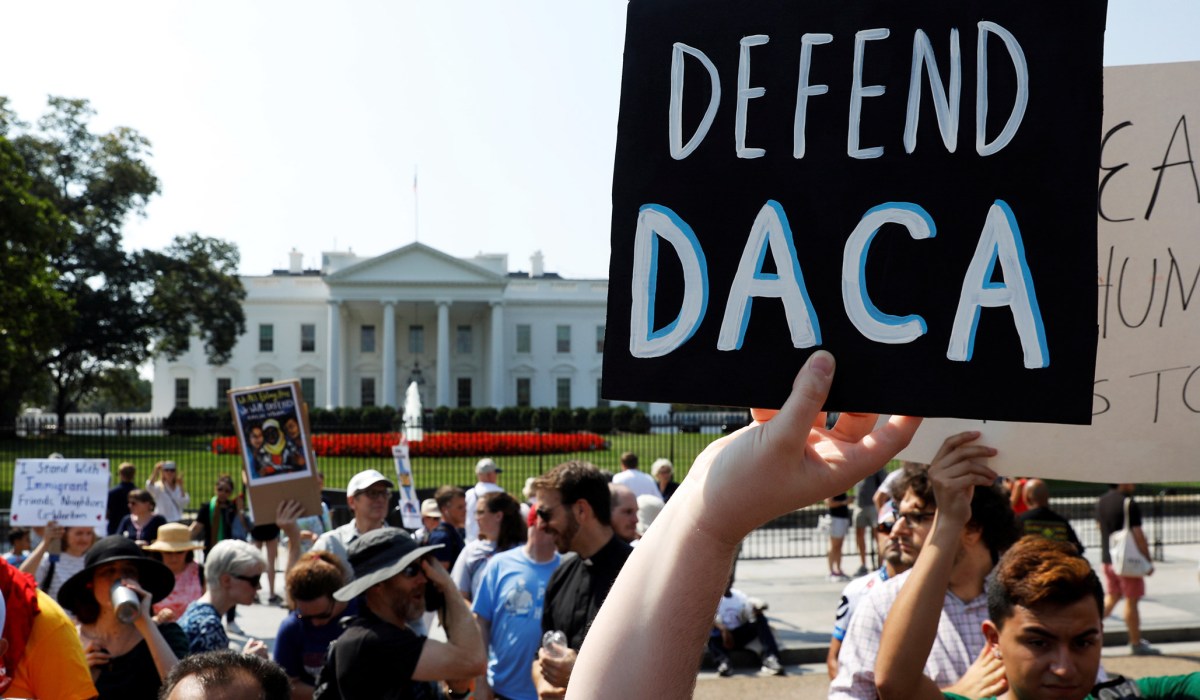
The 9th Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that Trump’s decision to phase out the Obama-era DACA program, which allows roughly 700,000 undocumented immigrants brought to the U.S. as children to obtain work permits and protects them from deportation, was likely “arbitrary, capricious, or otherwise not in accordance with law.”
Read more here.








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed